21st June 2024
Emotional Intelligence (EI) involves recognizing and managing both our own emotions and those of others. It’s crucial for navigating situations under pressure, such as giving feedback, meeting deadlines, handling difficult relationships, coping with limited resources, adapting to change, and overcoming setbacks and failures. EI helps us understand how emotions influence behavior and enables us to effectively manage them in various challenging circumstances.
The concept of emotional intelligence was coined by Peter Salovey and John Mayer in their 1990 article titled “Emotional Intelligence” in the journal Imagination, Cognition, and Personality. It gained broader recognition and popularity through Daniel Goleman’s 1995 book titled “Emotional Intelligence.”
Source : Daniel Goleman
Emotional intelligence is crucial for both personal and professional success due to its profound impact on how we navigate and interact with the world. Emotions, which often precede rational thought, can significantly influence our cognitive abilities, decision-making processes, and interpersonal skills. Here’s why emotional intelligence matters:
Personal Level:
– Facilitating Difficult Conversations: Enables us to handle sensitive discussions with empathy and tact.
– Stress Management: Helps in maintaining composure and clarity during stressful situations.
– Enhancing Relationships: Improves communication and understanding in personal relationships.
Professional Level:
– Conflict Resolution: Enables effective management and resolution of conflicts in the workplace.
– Coaching and Motivation: Empowers leaders to inspire and support their teams effectively.
– Fostering Collaboration: Cultivates an environment where teamwork and cooperation thrive.
– Building Psychological Safety: Establishes trust and openness within teams, encouraging innovation and growth.
Overall, emotional intelligence empowers individuals to navigate challenges with resilience, empathy, and strategic thinking, fostering both personal well-being and organizational success.
Daniel Goleman’s book “Working With Emotional Intelligence” emphasizes the growing importance of Emotional Intelligence (EI) in determining workplace success. According to research cited from Harvard Business School and Harvard Business Review, EI is twice as impactful as IQ and technical skills combined. Specifically, 80% of the competencies that differentiate top performers from others are linked to EI. This highlights that while intellectual and technical abilities are essential, EI—encompassing emotional management, social skills, and relationship-building—is increasingly recognized as the key to productivity, effective leadership, and organizational success.
Examples of EI in the workplace
Here are specific ways you might use emotional intelligence at work:
During a phone call
During a phone call, your client expresses frustration about the campaign’s performance and dissatisfaction with your partnership. Given their organization’s layoffs and their role in selecting team members for dismissal, you recognize the need for empathy. You calmly listen to their concerns and schedule another call for a more suitable time.
During a meeting
During a meeting, you notice your employee is unusually quiet and not participating in the discussion. Concerned, you decide to have a casual conversation with them to check in. It turns out they had a rough night because their mother-in-law is ill, affecting their focus.
During project review
After receiving constructive criticism during the project review, I initially felt deflated and anxious, given the effort I had invested. However, upon reflection, I recognized that dwelling on negativity wouldn’t help. Instead, I shifted my mindset to use the feedback as motivation to improve my next project.
Emotional intelligence (EI), also known as emotional quotient (EQ), encompasses the ability to understand and manage emotions effectively. Those with high EI can navigate interpersonal relationships empathetically, which is crucial for achieving professional goals and fostering a positive work environment.
Five components of emotional intelligence at work
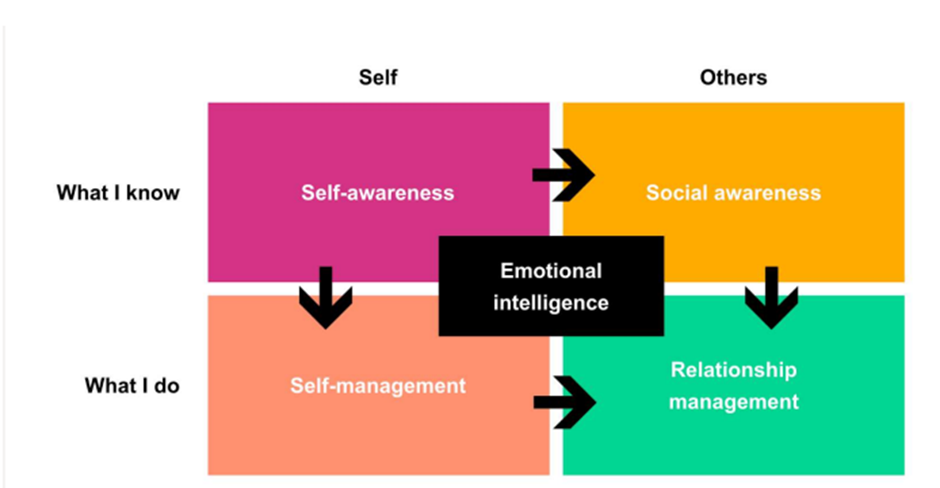
Daniel Goleman is indeed renowned for his work on emotional intelligence (EI) and its application in the workplace. He identified five components of EI, also known as emotional competencies, which are crucial for success in professional settings:
1. Self-awareness
Recognizing one’s own emotions and how they affect thoughts, behaviors, and performance. For example, a manager who understands their own strengths and weaknesses can effectively delegate tasks that align with their team’s abilities.
2. Self-regulation
Managing one’s emotions constructively and adapting to changing circumstances. This might involve staying calm under pressure during a crisis or controlling impulses to make reasoned decisions.
3. Motivation
Harnessing emotions to drive towards goals, persisting in the face of setbacks, and maintaining optimism. An employee who is intrinsically motivated strives for excellence and inspires others through their enthusiasm.
4. Empathy
Sensing others’ emotions, understanding their perspectives, and responding empathetically. This skill helps in building rapport with colleagues, resolving conflicts diplomatically, and providing effective customer service.
5. Social skills
Managing relationships to move people in desired directions, including communication, collaboration, and leadership. Leaders with strong social skills can inspire and motivate teams, negotiate effectively, and foster a positive work culture.
Improving Skills For Emotional Intelligence
Given below are some tips that can help you improve your skills for developing emotional intelligence:
1. Self-management
Successful self-management hinges on organization, beginning with a structured schedule and a healthy lifestyle. Managing stress is crucial, aiding focus in both personal and professional settings. Enhance self-management by seeking feedback, aligning actions with personal values, acquiring new skills, taking accountability, fostering emotional resilience, and setting achievable goals with clear deadlines.
2. Self-awareness
To manage emotions effectively and prevent them from clouding judgment, start by understanding their triggers. Enhance self-awareness by acknowledging feelings, viewing challenges as learning opportunities, refining communication skills, realizing responses are choices, and developing coping strategies for complex emotions.
3. Social awareness
Enhance social awareness by practicing conflict resolution, active listening, asking open-ended questions, showing genuine interest in others, and giving compliments regularly. These actions improve empathy and understanding of others’ emotional responses.
4. Relationship management
Improving emotional intelligence enhances relationship management skills through increased self-awareness and empathy. Strengthen these skills by sharing feelings openly, practicing perspective-taking, observing body language, and engaging in active listening. These actions foster healthier and more enduring relationships.
5. Social skills
Social skills like communication, empathy, interpersonal interactions, and listening are crucial in both personal and professional contexts. Enhance these skills by observing colleagues, maintaining eye contact, using icebreakers to initiate conversations, and asking open-ended questions. These improvements facilitate effective workplace interactions, planning, and collaboration.
How to improve emotional intelligence :
Use the following steps to improve your emotional intelligence both at and outside of work:
1. Be more self-aware
Improving emotional intelligence involves being aware of your own emotions and how they affect interactions. Track and analyze strong emotions, noting triggers and responses to enhance awareness and promote healthier communication and outcomes.
2. Recognize how others feel
Emotional intelligence begins with self-reflection and extends to understanding how others perceive your behavior and communication. Adapting your message based on how it’s received demonstrates emotional intelligence. Seek feedback from others to show that you value their reactions and prioritize effective communication.
3. Practice active listening
Effective communication involves paying attention to both verbal and nonverbal cues. Actively listening and observing reactions—both positive and negative—demonstrates respect and fosters healthy relationships. Show active listening by asking clarifying questions, nodding to acknowledge understanding, and summarizing key points to ensure comprehension. These actions enhance communication and strengthen interpersonal connections.
4. Communicate clearly
Effective communication is pivotal in emotional intelligence, encompassing knowing what, when, and how to convey information to build robust relationships. For instance, as a manager, clearly communicating expectations and goals ensures alignment within the team. Foster open communication channels to encourage others to express their feelings and thoughts freely, enhancing collaboration and understanding in the workplace.
5. Stay positive
Emotionally intelligent individuals recognize the impact of positivity through encouraging words, supportive emails, and gestures of kindness. Maintaining a positive demeanor in stressful situations can help others stay calm and foster problem-solving and teamwork. While acknowledging that negative emotions are natural, develop strategies to mitigate their impact and focus on finding constructive solutions. This approach promotes a supportive and productive environment for everyone involved.
6. Empathize
Empathizing with others’ emotions is a key aspect of emotional intelligence, enabling respectful and comforting responses. Put yourself in their shoes to understand their feelings and respond empathetically. This perspective helps build stronger connections and fosters supportive interactions based on understanding and consideration.
7. Be open-minded
Emotionally intelligent individuals are approachable due to their attentive listening skills and ability to understand diverse perspectives. They are receptive to new ideas and continuous learning. Even when uncertain about a new concept, they strive to envision its practical implementation in daily work, fostering innovation and growth within their teams and organizations.
8. Listen to feedback
Being receptive to feedback, whether positive or constructive, is essential for personal and professional growth. It demonstrates accountability and a willingness to enhance communication and effectiveness. While feedback can sometimes be difficult to accept, viewing it as a learning opportunity fosters continuous improvement and professional development. This mindset not only improves individual performance but also strengthens relationships and contributes to overall success in various endeavors.
9. Stay calm under pressure
Maintaining a calm and positive attitude during stressful situations is crucial for effective problem-solving and goal achievement, especially under deadlines. Strategies such as deep breathing and seeking assistance can help manage stress and maintain focus on finding solutions. These approaches not only contribute to personal resilience but also promote a supportive and productive team environment conducive to meeting collective objectives.
Why is emotional intelligence important? Emotions play a significant role in daily decision-making, and having a high emotional intelligence (EQ) enables one to understand others’ emotions, manage and express their own effectively, build healthy relationships, and solve problems efficiently even under pressure. Employers who possess high EQ skills often excel in problem-solving and decision-making, contributing to effective leadership and organizational success.
Consequences of a low EQ
Low workplace EQ can lead to several negative consequences:
1. Lack of Emotional Accountability: Employees may struggle to take responsibility for their emotions and actions.
2. Poor Team Dynamics: Collaboration and teamwork may suffer due to difficulties in understanding and managing emotions.
3. Ineffective Communication: Communication between employees and management may be ineffective, hindering clarity and alignment.
4. Inefficient Decision-Making: Decisions may be made impulsively or without considering emotional factors, leading to suboptimal outcomes.
5. Reduced Productivity: Emotional barriers can impact focus and efficiency, resulting in decreased overall productivity.
6. Poor Problem-Solving: Difficulty in managing emotions and collaborating effectively can impede creative problem-solving.
7. Challenges with Feedback and Development: Employees may struggle to receive and provide constructive feedback, limiting personal and professional growth.
8. Increased Turnover and Hiring Costs: A negative workplace culture stemming from low EQ can contribute to higher employee turnover and increased costs associated with hiring and training new personnel.
In workplaces with low EQ, teamwork can be hindered, accountability may be lacking, communication may falter, and productivity may suffer, ultimately impacting both business performance and employee morale.
Why is emotional intelligence important in the workplace?
Since its discovery in the 1990s, emotional intelligence has emerged as a crucial factor for workplace success. Researchers have consistently found that emotional intelligence:
– Enhances relationships among colleagues,
– Enables effective management of conflict and stress,
– Improves overall work performance,
– Increases job satisfaction.
Companies with employees who possess high emotional intelligence are more likely to cultivate strong and capable teams. These teams are adept at minimizing conflict and consistently demonstrate outstanding productivity and performance. Emotional intelligence plays a pivotal role in creating a collaborative and supportive work environment where individuals can thrive and contribute effectively to organizational success.
Emotional intelligence examples in the workplace
Companies with employees who possess high emotional intelligence are more likely to cultivate strong and capable teams. These teams are adept at minimizing conflict and consistently demonstrate outstanding productivity and performance. Emotional intelligence plays a pivotal role in creating a collaborative and supportive work environment where individuals can thrive and contribute effectively to organizational success.
1. Responding positively to new initiatives
Displaying emotional intelligence in the workplace involves showing readiness to take on new initiatives or projects with a positive attitude. By demonstrating understanding of your supervisor’s expectations and showing willingness to complete tasks effectively, you can enhance relationships and earn more responsibilities. Additionally, asking thoughtful questions to clarify responsibilities and understand processes further demonstrates your commitment to success and your ability to navigate new challenges with confidence.
2. Communicating effectively
Demonstrating emotional intelligence in communication involves speaking clearly and respectfully to co-workers and employers. By choosing words carefully and considering colleagues’ feelings before speaking, you can foster productive conversations and build stronger relationships. Effective communication also entails refraining from negative or critical remarks, as you understand their potential to lower morale and disrupt teamwork. This approach not only enhances workplace harmony but also promotes a positive and supportive environment conducive to achieving common goals.
3. Being flexible
Demonstrating emotional intelligence involves adapting swiftly to changing situations without waiting for input from superiors. Understanding the reasons behind these decisions and showing empathy towards those affected reflects positively on you. This proactive approach can increase colleagues’ trust in your ability to deliver and adjust to evolving conditions. Additionally, offering assistance to colleagues by taking on their tasks promotes a supportive atmosphere and encourages mutual cooperation, fostering a culture of teamwork and readiness to help one another as needed.
4. Socialising and networking
Socializing outside of work with colleagues and employers can significantly enhance personal and professional relationships. It provides opportunities to better understand each other, which can be especially valuable in diffusing tensions caused by work challenges. By fostering a deeper connection, socializing helps improve communication, support, and camaraderie in the workplace, ultimately contributing to a more positive and collaborative environment.
5. Providing emotional support
Demonstrating empathy towards colleagues fosters trust and encourages them to confide in you about their challenges. By actively listening and assisting in finding constructive solutions, you showcase emotional intelligence. This ability not only strengthens relationships but also highlights your potential for leadership by effectively understanding and managing others’ emotions, thereby promoting a supportive and cohesive team dynamic.
6. Listening actively
Active listening demonstrates respect for the speaker and empathy towards their emotions. This skill is crucial during meetings, discussions with colleagues, or addressing customer complaints, as it enables you to accurately perceive and effectively respond to others’ feelings and concerns. By actively listening, you build trust and strengthen relationships by showing genuine interest and understanding in what others have to say, fostering a supportive and communicative environment.
7. Taking on challenges
Offering assistance to supervisors or colleagues demonstrates your proactive nature and commitment to teamwork, portraying you as a highly productive individual and a valuable team player. Additionally, actively seeking opportunities to develop essential skills and knowledge shows your dedication to personal growth and career advancement. By continuously expanding your capabilities and contributing effectively in various roles, you enhance your versatility and position yourself for professional success and advancement.
8. Dressing and acting intelligently
When preparing for job interviews, thorough research on the company and familiarizing yourself with common interview questions is essential. Dressing professionally demonstrates your ability to represent the company both intellectually and physically, which is particularly important for in-office roles. This preparation not only showcases your preparedness and enthusiasm but also enhances your chances of making a positive impression on potential employers.
9. Taking on the role of a leader
As a professional, demonstrating leadership often requires maintaining calmness and self-control in challenging situations, showcasing emotional intelligence. Developing leadership qualities can be further enhanced by participating in leadership conferences and clubs, where you can learn and network with other leaders. These opportunities notonly help refine your leadership skills but also provide valuable insights and strategies for effectively managing and guiding teams or projects.
10. Supporting others
Displaying high emotional intelligence involves consistently supporting others, regardless of your own circumstances. This may include assisting colleagues with their tasks, contributing to project completion, or providing emotional support. By actively helping others succeed, you nurture strong relationships in the workplace. Additionally, sharing career growth opportunities with colleagues demonstrates your commitment to their professional development, fostering a collaborative and supportive environment where everyone can thrive. These actions not only showcase your emotional intelligence but also contribute to a positive and cohesive team dynamic.
11. Taking responsibility for your mistakes
When confronted with challenges, taking responsibility instead of assigning blame is a hallmark of emotional intelligence. Reflecting on past actions to understand their role in the situation helps prevent similar issues from arising in the future. Learning from these experiences improves your ability to handle future challenges effectively and fosters personal and professional growth. This approach demonstrates accountability and a proactive mindset, contributing to continuous improvement and resilience in overcoming obstacles.
12. Handling criticism maturely
Demonstrating high emotional intelligence involves accepting criticism with enthusiasm and using it constructively to make necessary changes. Embracing feedback effectively supports personal and professional growth by fostering continuous improvement. In addition to receiving criticism positively, providing constructive feedback to colleagues when appropriate also demonstrates emotional intelligence. This approach not only helps others improve but also strengthens relationships and promotes a culture of mutual support and development within the workplace.
Key Takeaways:
– Emotional intelligence is crucial for enhancing interpersonal relationships, whether in personal or professional settings.
– The five components of emotional intelligence at work are self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills.
– Benefits of emotional intelligence in the workplace include improved understanding of nonverbal cues, effective behavioral adjustments, sound decision-making, and the ability to earn respect as a leader.